Diabetes
What is Diabetes
Diabetes Mellitus, one of the most talked about diseases, possesses an enormous health problem across the world. Anyone, from any walk of life can get Diabetes and the numbers of those being diagnosed seem to be on the rise. It poses to be one of the fastest growing health challenges of the 21st century. This epidemic, if unchecked, can not only affect the health and wellbeing of the general population, but can also impact the economy of countries at large. Education therefore not only plays a role in creating awareness, but also in prevention of the disease and its various complications.
So, what exactly is Diabetes?
Diabetes Mellitus is a disease which is characterised by chronically elevated levels of sugar in the blood due to either an absence of, or resistance to Insulin.
Insulin is the hormone responsible for keeping your sugar levels in check. Without Insulin, Glucose, the primary fuel responsible for providing energy to all cells in the body is unable to be delivered into the cells resulting in excess accumulation of Glucose in the bloodstream. This leads to damage of blood vessels throughout the body.
So, if you want to treat this condition, you will need to get in touch with a diabetes nutritionist who can help you manage the condition through a holistic diabetes management programme where you’ll be recommended a good diet, exercise, and other lifestyle changes essential for your condition.
Need to consult?
Quickly Book an Appointment.
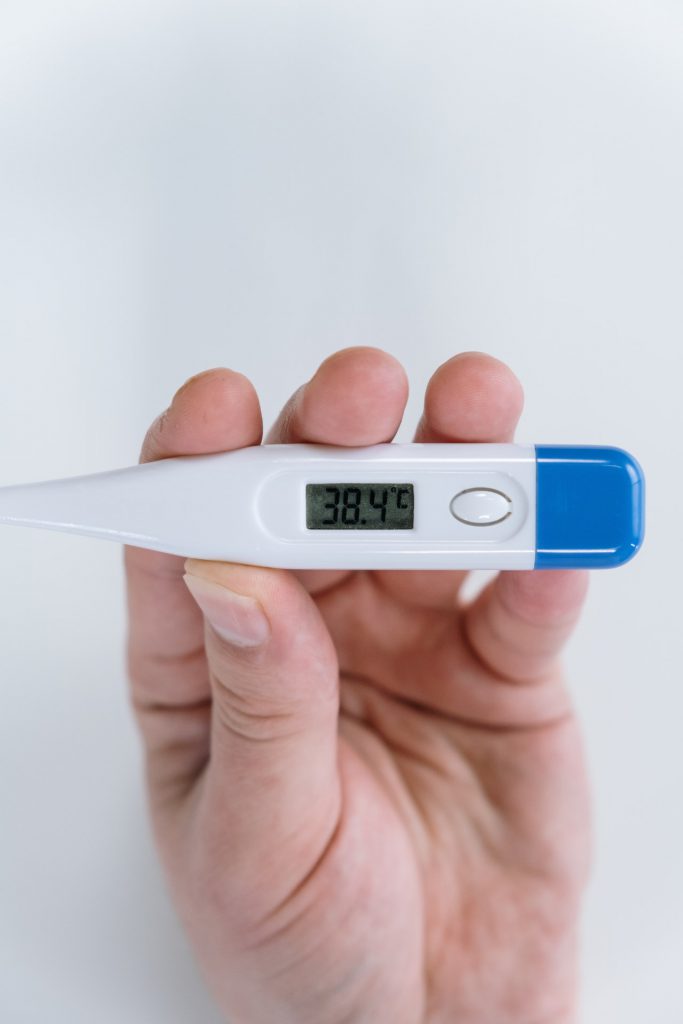
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
The three known different types of Diabetes Mellitus are:
- Type I Diabetes Mellitus (also previously known as Juvenile onset Diabetes or Insulin Deficiency disease) : In this Autoimmune disease, the immune system itself destroys the Insulin producing beta cells of the Pancreas, as a result of which, the body can no longer produce its own insulin. Type I diabetes is less common than type II Diabetes – approximately only 5-10% of people diagnosed with Diabetes have Type 1 Diabetes.
- Type II Diabetes Mellitus (also known as Adult onset Diabetes or Insulin resistance disease) : Type II Diabetes, the most common form of Diabetes accounts for around 90% of all Diabetic cases and is usually a part of a metabolic syndrome cluster.
In Type II Diabetes, the Pancreas produces Insulin, however this Insulin produced does not work as efficiently as it should. Its action is impaired by the accumulation of fat within the cells of the muscles and liver and this inability of the cells to respond to Insulin is known as Insulin resistance.
Type II Diabetes is generally diagnosed in middle aged or older individuals, however it can also affect kids and teenagers owing to childhood obesity.
- Prediabetes: Prediabetes occurs when the blood glucose levels are elevated but not high enough to be classified as Diabetes. It is often a precursor of Type II Diabetes if appropriate intervention is not taken to prevent the progression. Remember you can still go back to your normal insulin levels with a proper diet. So if think your blood sugar is at the border line, then get in touch with the top prediabetes nutritionist.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus : It is characterised by elevated blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally subsides after delivery, however it can affect the baby’s health, and it raises the mother’s risk of developing Type II Diabetes later in life.
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes and Risk factors of Type 1 Diabetes
The exact cause of Type I Diabetes is unknown. In some people, genes may be responsible whilst in others, a virus could possibly set off the immune system attack where it can mistakenly attack the insulin producing beta cells of the pancreas.
Risk factors:
- Family history : Anyone with a family history of Type I Diabetes like a parent or sibling generally has a slightly increased risk of developing the disease.
- Genetics : Having certain genes may increase the risk of developing Type II Diabetes.
- Age : Although type 1 diabetes can occur at any age, it appears usually at two noticeable age peaks. The first peak occurs in children aged between 4 and 7 years whereas the second occurs in children aged between 10 and 14 years. Developing Type I Diabetes in later years is usually rare.
Causes and Risk factors of Prediabetes and Type II Diabetes
Type II Diabetes is usually caused by a combination of different factors. Having certain predispositions makes some individuals more prone to developing Type II Diabetes. They are:
- Family History : Anyone with a family history of Type II Diabetes like a parent or sibling generally has a slightly increased risk of developing the disease.
- Genetics
- Age : 45 or older
- Obesity
- Metabolic syndrome : Cluster of different medical conditions such as elevated blood pressure, cholesterol, triglyceride levels, prediabetic and obesity.
- Ethnicity : Asian , African American, Native American, Alaska Native, Hispanic, or Pacific Islander American
- Gestational diabetes during pregnancy
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Depression or stress
- Lack of physical activity
- Smoking
- Irregular sleeping and waking up schedule
Causes and Risk factors of Gestational Diabetes
Why some pregnant women develop Gestational Diabetes whilst others don’t is still at large unknown.
Risk factors include:
- Excess weight and unhealthy lifestyle before pregnancy are attributed as definite contributing factors.
- Family history of Diabetes
- History of Gestational Diabetes during the previous pregnancy term
- Having previously delivered an infant with a high birth weight
- Personal history of PCOD or Prediabetes or both
- Ethnicity: Asian , African American, Native American, Alaska Native, Hispanic, or Pacific Islander American
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of Type 1 and Type II Diabetes
Signs and symptoms of Type I Diabetes are generally subtle initially, however, they can become severe, whereas in the case of Type II Diabetes, the symptoms slowly develop over several years. They include:
- Increased hunger (especially even after eating)
- Extreme thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained and unintended weight loss,
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Upset stomach and vomiting
- Blurry vision
- Labored breathing
- Frequent infections of your skin, urinary tract, or vagina
- Mood changes and irritability
- Bedwetting in a child who has no history of wetting the bed during the night (Generally In case of Type I Diabetes)
- Breath: Fruity smell
If you’re facing these symptoms, please feel free to contact our registered dietitian for diabetes.
Symptoms of Prediabetes and Gestational Diabetes
Prediabetes and Gestational diabetes typically may not cause any noticeable signs or symptoms of Diabetes. Increased thirst or increased urination may be noticed, rarely.
Complications
Complications of Type I and Type II Diabetes
Excess accumulation of glucose in the blood can lead to damage of blood vessels throughout the body thereby affecting several organs and tissues. Listed below are some of the complications associated with Diabetes:
- Diabetic Neuropathy (Nerve damage which leads to numbness, tingling and pain sensation, poor circulation of blood flow to the legs and feet, resulting in poorly healing wounds)
- Diabetic Nephropathy (Kidney damage)
- Diabetic Retinopathy (Damage to blood vessels of the Retina) and vision loss
- Cardiovascular complications like heart disease, heart attack, and stroke
- Hearing impairment and loss
- Bacterial and fungal infections
- Depression and stress
- Dementia
Complications of Prediabetes
Prediabetes can progress into Type II Diabetes
Complications of Gestational Diabetes
Some of the complications for the mother are:
- Greater chance of needing a Cesarean birth (C-section) possibly due to large infant size.
- Increased risk of preeclampsia
Increased risk of developing Type II Diabetes post pregnancy
Diagnosis
The following tests are generally used to diagnose Diabetes:
- Fasting plasma glucose test: It is done after fasting for 8 hours to measure the blood glucose levels. It is usually used to detect Diabetes and Prediabetes.
- An oral glucose tolerance test :75 g of glucose dissolved in water is given orated or through IV after fasting plasma glucose test, and it is taken at specific intervals. Normal post prandial upper limit is 140 mg/dl. Used to detect Diabetes or Prediabetes.
- Random plasma glucose test :This is done to check blood sugar levels without regard to when the last meal was consumed. This test, along with an appropriate assessment of symptoms, is used generally to diagnose diabetes, but not prediabetes.
- A hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test:It is done to diagnose or confirm either prediabetes or diabetes and can be done without fasting
| Type of Test | Normal | Prediabetic | Diabetic |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBA1C | Below 5.7 % | 5.7-6.4 % | Above 6.5 % |
| Fasting sugar levels | 70-99 mg/dl | 100-125 mg/dl | Above 125 mg/dl |
| Post prandial sugar levels | Less than 140 mg/dl | Less than 180 mg/dl | |
| Random sugar levels | More than 200 mg/dl |
Prevention and Treatment
Prevention and Treatment of Type I Diabetes
Type I Diabetes cannot be prevented, neither can it be cured. However, it can be successfully treated and managed by following Doctor’s and Clinical Dietitian’s recommendations on maintaining optimum blood sugar levels and living a healthy lifestyle.
People diagnosed with Type I Diabetes can live long and healthy lives by keeping a close check on their blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
The medical treatment requires Insulin shots or Insulin pump, a form of hormone replacement therapy to make up for the lack of production of Insulin.
Apart from administration of medical treatment, inculcating healthy lifestyle habits such as those mentioned below are also crucial for optimum Type 1 Diabetes care and management.
- Making healthy food choices
- Being physically active
- Managing stress
- Controlling blood pressure
- Controlling cholesterol levels
- Scheduling regular appointment with health care teams to monitor progress
Enroll in our diabetes care programme to get the best results!
Prevention and Treatment of Prediabetes, Type II Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes
Several studies have proven that with adequate lifestyle modifications like obtaining healthy weight loss by eating healthy and being physically active can dramatically help reduce the progression of Prediabetes, Type II Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes and can also minimize the effects of other Diabetes related risk factors and complications.
With routine dedication and time, Prediabetes, Type II Diabetes can be reversed owing to significant long term improvement in insulin sensitivity. However, due to lack of awareness, less than 0.1 % of people diagnosed are recorded to be in remission. Consulting a doctor and clinical dietitian about the possibility of reversing Prediabetes, Type II Diabetes through healthy weight loss is recommended. For most women diagnosed with Gestational Diabetes, post delivery, it goes away.
A diabetes management programme and medical treatment involves a combined strategic involvement of medications and lifestyle modifications such as :
- Medications :Taking prescribed oral medications or insulin (In progressive disease condition) post consultation with a doctor.
- Weight loss: Dropping extra weight can prove to be helpful . Losing even about 5-10 % of current body weight can help in improving insulin sensitivity. However, losing around 10-15 % is ideal.
- Healthy eating: Consuming a diet which focuses on complex carbohydrates, low fat dairy products, low GI fruits and vegetables and adequate dietary fiber has tremendous positive impact on the improvement of the disease condition.
- Physical activity :Regular physical activity such as a minimum 20-30 minutes of short bursts of exercise daily can help improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitoring of blood sugar levels as recommended by the doctor.
- Watson, S. (2020, February 27). Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Prevention, and More. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/diabetes
- An overview of type 1 diabetes. (2003, January 24). Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/type-1-diabetes
- www.ETHealthworld.com. (2016, January 28). India is the diabetes capital of the world! Retrieved from https://health.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/diagnostics/india-is-the-diabetes-capital-of-the-world/50757875
Food & Wellness | Diabetes Management Programme
At Food & Wellness, the diet plans are tailor made and customised by an expert panel of Nutritionists to ensure that the progression of the above existing medical conditions are slowed down and overall health parameters are gradually improved over the course of time.
In detail discussion of your Dietary and lifestyle habits along with scientific analysis of blood reports is done to further support the holistic management and treatment of disease ailments.
Through the Diabetes management program, we aim to positively improve the Diabetes disease profile by significantly decreasing the initial body weight, fasting and post prandial blood sugar levels through provision of easy to follow and flexible dietary and lifestyle recommendations with key emphasis on suggesting a variety of food options to break the cycle of meal monotony.
Post conclusion of the program, Maintenance diet plans are assigned to encourage adoption of healthy eating principles and of inculcating a nourishing and healthy lifestyle, all of which are taught during the course of the program.
This advocates and ensures that the individual remains healthy throughout life.
To know more on how to manage your Disease profile, subscribe to Food & Wellness blog today!

Let's get started with treating your condition...
At Food & Wellness we believe that every individual is different and needs special attention. We adapt our programme to your existing lifestyle and try not to change anything drastically so you can easily transition. Over a period of time we ensure results and help you restore your health.
Diabetes Articles

The Hidden Link Between Insulin Resistance, Fatty Liver, and Cholesterol
The hidden link between insulin resistance, fatty liver, and cholesterol is something many people live with for years without realising it. Blood sugar may look “slightly high,” cholesterol numbers may be borderline, and an ultrasound may quietly mention fatty liver. These problems often appear separate, but in reality, they are deeply connected.

Sprouted vs. Unsprouted Grains: A Scientific Comparison for Optimal Nutrition
Sprouted grains are nutritionally superior to unsprouted grains thanks to enhanced digestibility, higher antioxidants, reduced antinutrients, and improved glycemic control. This article explores the biochemical changes during sprouting and provides practical dietary recommendations based on recent scientific research.
Oral Health and Wellness: The Mouth-Body Connection
Your mouth is a mirror of your overall health. Poor oral hygiene can lead to chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s—learn how to protect yourself.
